Your cart is currently empty!

Traditional Medicine & Herbalism
Traditional medicine has been a cornerstone of healthcare worldwide for thousands of years, with practices rooted in the cultural and historical contexts of various regions. From the ancient civilizations of China and India to the indigenous cultures of Africa and the Americas, traditional medicine has evolved to incorporate local flora, fauna, and spiritual beliefs into holistic approaches to health and wellness. This rich tapestry of traditional medicine includes practices such as acupuncture, Ayurveda, and herbalism, which have been passed down through generations and continue to play a significant role in modern healthcare. Despite the rise of modern medicine, traditional medicine remains an essential part of many cultures, offering a unique blend of natural remedies, spiritual practices, and community-based care that complements and enhances contemporary healthcare systems.
Modern medicine has eminences in quick effect, specific, rational, with an onset of side effects and common symptoms remedy application. Traditional medicine has slow effects, but by considering to use of the whole specimen, it minimizes or even erases the side effects. Practice of Traditional medicine also gain more by considering the uniqueness of their patient body type and their mental-spiritual side, which modern medical care nowadays, lamentably grows more and more apart from it and puts emphasis only on the body. Traditional medical practice believes that “Spiritual comes first, then what is material.” However, no doubt, the combination of both practices is the most beneficial. For example, modern medicine is best for a critical moment and traditional medicine is needed later for recuperation, or best, to maintain the body-mind health from falling into the same sickness again.
Two of the most popular ancient & holistic medical systems practised today: Chinese Medicine (TCM) & Ayurveda
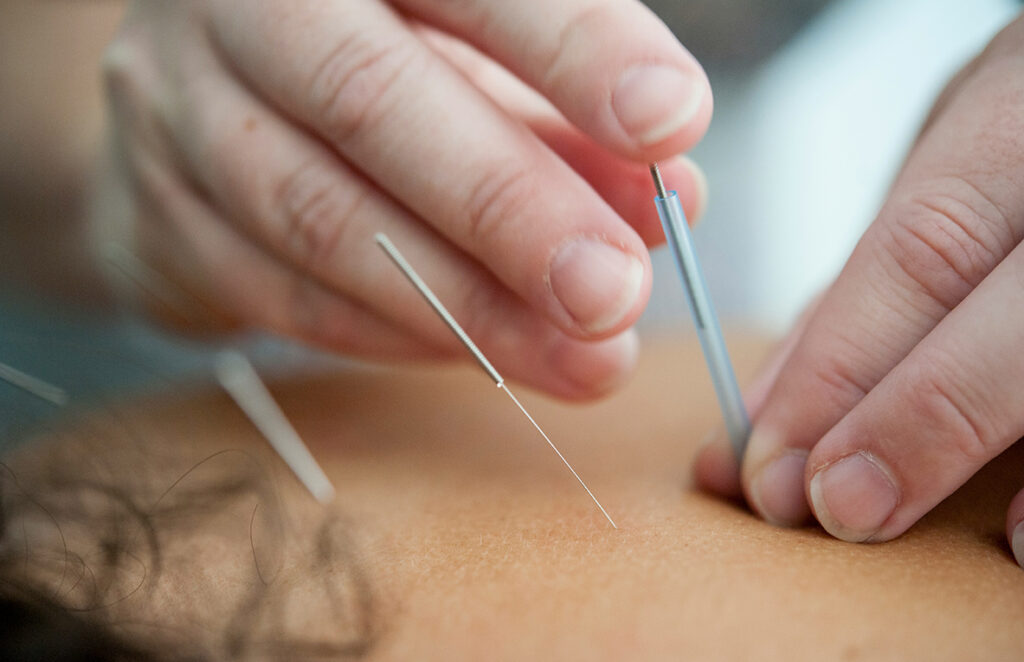
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
TCM, originating from China, emphasizes the balance of Qi, a vital energy that flows through the body, to maintain health and prevent disease. It includes various therapies such as acupuncture, moxibustion, massage, and herbal medicine.
TCM consider the Taoism mindset that all creation should be in harmony, thus the goal is to harmony the human being’s body and spirit with the whole creation. Chinese Medicine practice considers each type of patient as unique by including their body type’s elements reading. The five element types are Earth, Metal, Water, Wood, and Fire. TCM experienced Lǎoshī, by years of practice, has the capability to accurately differentiate their patient constitutional by sight and even know which part of the body has dis-harmonized through a complex reading of the patient’s body’s symptom manifestations.

Ayurveda
Ayurveda, originating from India, focuses on the concept of three doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) that govern the functioning of the body and mind. It uses a combination of herbal remedies, diet, and lifestyle changes to balance the doshas and promote overall well-being. Likewise, traditional Chinese medicine, Ayurveda share a common philosophy of treating the whole person, including the physical, mental, and spiritual aspects: emphasizing the harmony between mind, body and soul through an appropriate practice of diet, lifestyle, and herbalism. It also has a unique point of view considering everybody has their own unique character, thus needing a different approach to heal.
The five elements believed to exist in Ayurveda practice are Earth, Water, Air, Fire, and Space. These elements’ combinations made the three types of energy couple or dosha. Everyone has three types of dosha but one of them is dominant, and the combination of doshas creates one’s physical constitution (Prakriti) & personality. To harmonize those doshas, Ayurveda medical practices meditation, yoga, diet, body care, massage, aroma therapy, breathing exercises, and many others.

Herbalism
Herbalism The Mother of Pharmacology: A Growing Field with a Long Tradition
Herbalism, also known as herbal medicine or phytotherapy, is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are the basis of traditional medicine. With worldwide research into pharmacology, some herbal medicines have been translated into modern remedies, such as the anti-malarial group of drugs called artemisinin isolated from Artemisia annua, a herb that was known in Chinese medicine to treat fever.
Herbalism has a long history, dating back thousands of years. It is the sum total of the practices based on the theories, beliefs, and experiences of different cultures and times, often inexplicable, used in the maintenance of health, as well as in the prevention, diagnosis, improvement, and treatment of illnesses.
Traditional Herbalism
Traditional practitioners use their senses to identify and recognise each specimen’s potential or property effects on the body. For example, they cut a small piece of a certain leaf and put it on their tongue. They discreetly write the specimen’s effects and indication on their body:
- Actions: the effect on the body tissue or organ.
- Energetics: the feeling inside the body.
- Users & Indications: the effect might slow, for example in 6 weeks or even more subtle, thus formulation is important.
- In identifying new herbal specimen potentials, some practise a spiritual or mental mindset that the whole character of the plant or creature is a certain symbolical presentation of God. Thus directing their mind and spirit to God in a certain quality like a prayer to receive a reply guidance from Him.
Practitioners of traditional herbalism gather their herbal ingredients either by wild crafting or growing their herbs. They put in mind to take no more than needed and to let the plant preserve its own life, such as no more than one-fourth or one-eighth of the stem collected.
Herbalism traditional practitioner preserves their herbs potent by drying them and or making an extraction using a tincture or percolation method. Some herbal outcomes might be for internal use or external use. The output varies from, salve, essential oils, tea or tisanes, syrups, and others.
Benefits of Herbal Medicine
Herbal medicine offers several benefits, including:
- Cost-Effective and Accessible: Herbal medicine can be a cost-effective option compared to modern medicine, especially when used in conjunction with other holistic practices. High-quality herbs should always be taken in controlled dosages as prescribed by a qualified naturopath.
- Natural Healing: Herbal medicine is a completely natural approach to prevention, healing, and health support. Used in the right dosage, and individually prescribed for your needs, they are a safe and effective way of, in some instances, opting away from or helping to support pharmacy medications.
- Mitigated Risk of Side Effects: Unlike a lot of pharmacy medications, there are far fewer side effects when herbal medicine is used as prescribed. Their formulations are designed to support and strengthen the body in an ongoing capacity. Despite their high efficacy, they have significantly fewer instances of dire reactions, dependency, and complications.
- Holistic Health: Herbal medicine is a holistic therapy, that integrates emotional, mental, and spiritual levels. Lifestyle, emotional, mental, and spiritual considerations are part of any naturopathic approach. The use of herbs does not generally involve “drug” actions or adverse effects.
- Empowerment: Herbal medicine offers autonomy, whether you are disillusioned with the modern medical system or simply want to be more in control of your health. Traditional healers provide their patients with the knowledge to prevent illness, manage their chronic conditions, and promote healing.
Herbalism is a complex and multifaceted field that has been practised for thousands of years. While it has the potential to provide effective treatments, it also carries risks and must be approached with caution. It is essential to educate oneself about herbal supplements and to consult with a professional traditional healthcare provider before using them.
Here are some further reading considerations for traditional medicine and herbalism. I also include a licensed and professional herbalism website where you can consult or find a certain herbs potent remedy.
- Modern Herbal Dispensatory by Thomas Easley and Steven Horne
- http://www.findanherbalist.com/
- http://www.mountaingardensherbs.com/
- Everyday Chinese Medicine by Mindi K.Counts, MA, LAc.
- Handbook of Medicinal Herbs by James A. Duke with Mary Jo Bogenschutz-Godwin, Judi duCellier, Peggy-Ann K. Duke
- Diagnosis in Chinese Medicine by Giovanni Maciocia
- https://ayurveda.com/ayurveda-a-brief-introduction-and-guide/


Leave a Reply